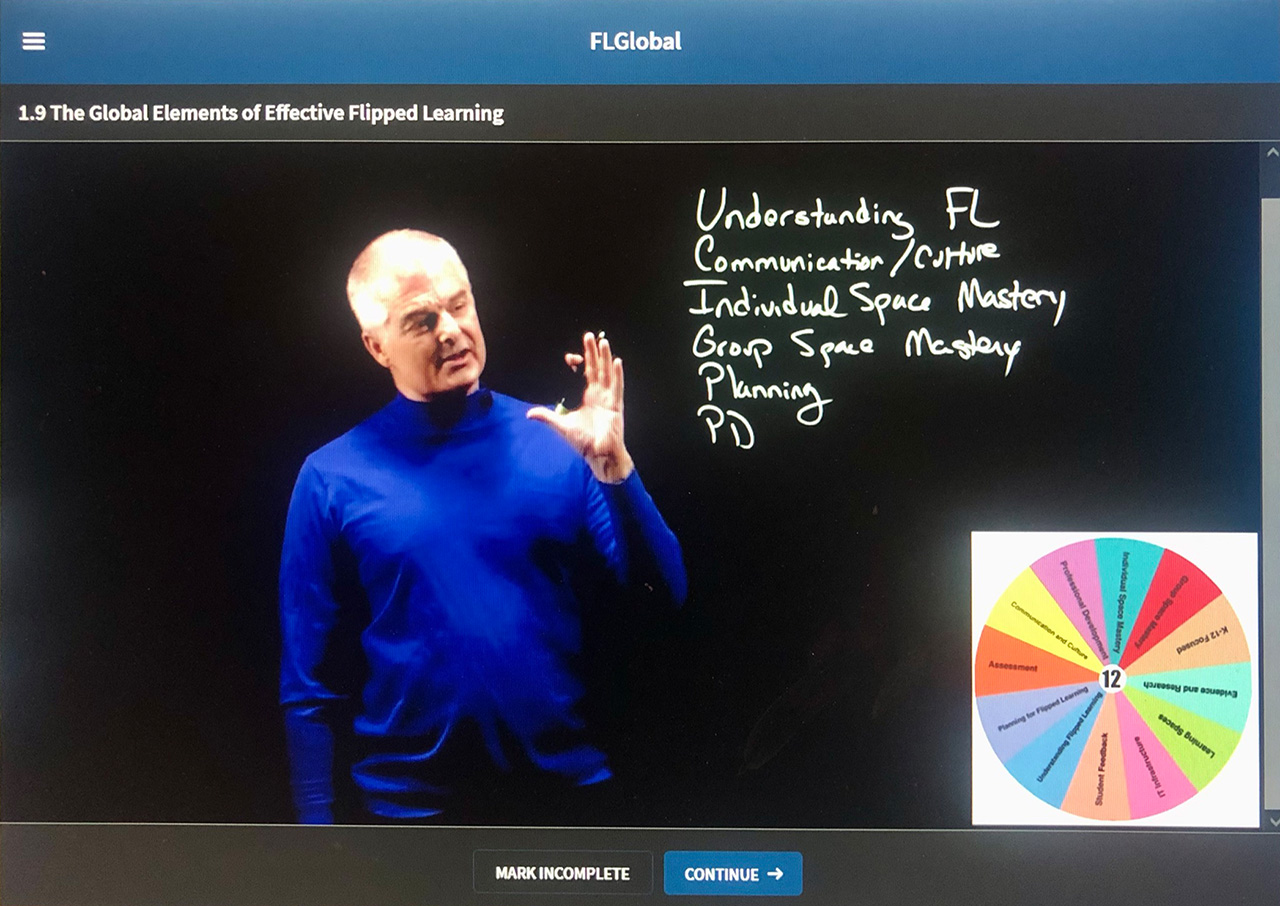
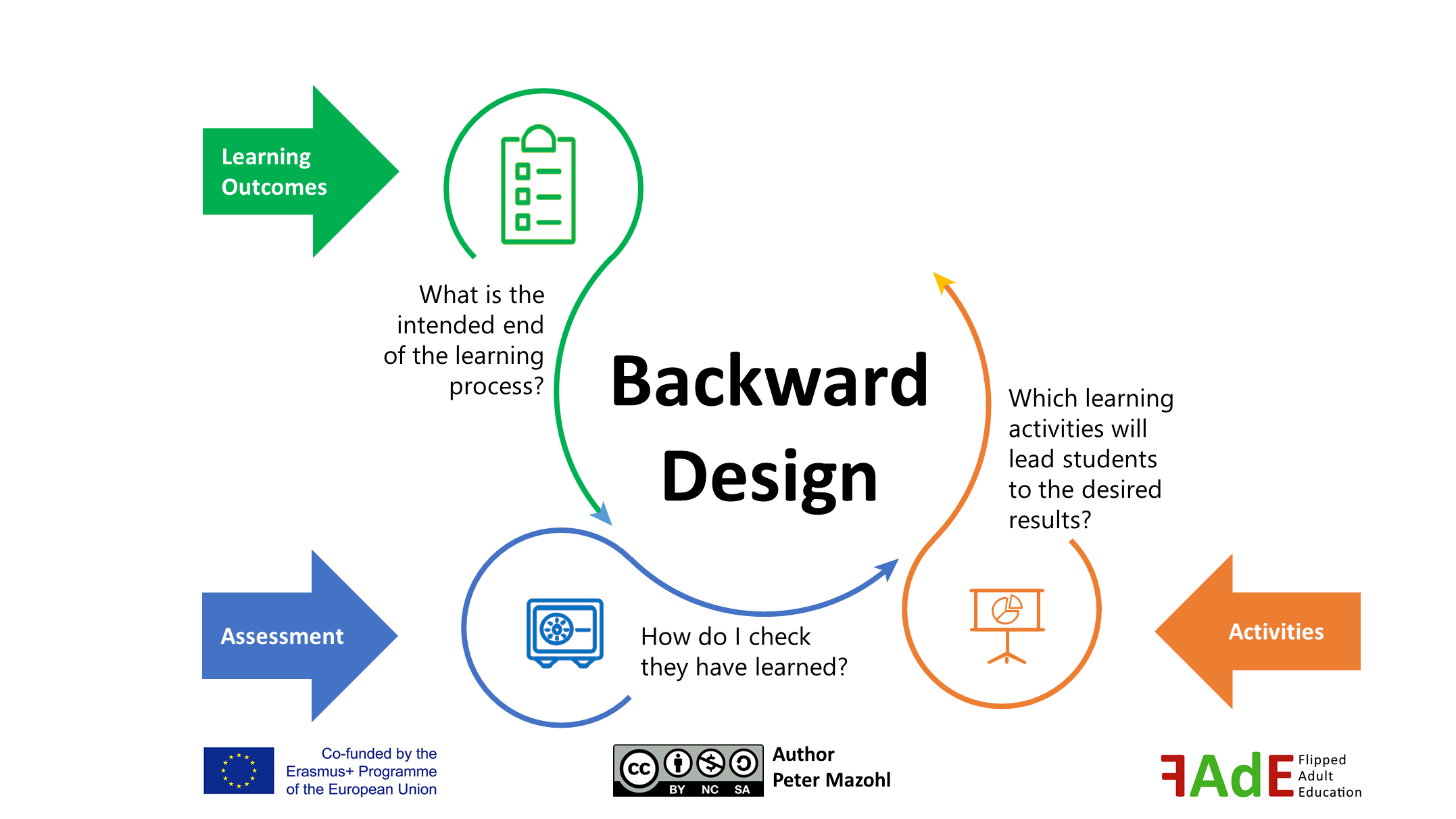
The Group Learning Space explained by a FAQ list
The Group (Learning) Space in Flipped Learning 3.0 is an essential component where trainees engage in activities that encourage higher-order thinking skills. Trainers need to prepare for the varied levels of understanding trainees bring to the Group Space, ensuring that there is room for questions, clarification, and addressing misconceptions. Key activities such as practice sessions, Read More …